Introduction to SharePoint
SharePoint is an extensible web based platform which
contains various products and technologies aimed at development of corporate
portals. These products and technologies are referred to as SharePoint Products and Technologies.
It allows
individuals in an organization to easily create and manage their own
collaborative Websites
- Simplifies how people find and share information across boundaries and enabling better informed decisions
- Seamlessly integrates with Windows and MS Office
Does not refer to a specific product or technology
- Using the word “Microsoft SharePoint” is like using the word “Microsoft Office”
Advantages of SharePoint Products and
Technologies (High level features)
- Rich UI
- Easy site editing and branding
- Ribbon Interface.
- Better Site Provisioning
o Quick development
o No DBA required
- Better document Management
- Better Versioning
- Document Libraries
- Document Column (Attachments)
- Check in / Check out
- Document Workflow (Approval)
- Document View within browser
- Permissions
- Automated Email and SMS Alerts
- Easy Customization options: “My Site” (using
WebParts)
- Built In Indexing & Search Engine
- Integration with Active Directory
- Integration of MS-Office Products
- Reports in PDF, Word and other formats
- Collaboration
- Communication
- Task Manager
Six
Pillars of SharePoint 2010
|
1.
Sites
2.
Communities
3.
Content
4.
Search
5.
Insights
6.
Composites
|
|
1. Sites: Building and Managing
Internal and External Websites
Think of SharePoint 2010 Sites as a “one-stop shop” for all business Web
sites. It provides a full set of tools that people can use to create any kind
of site, plus a single infrastructure that simplifies site management. From a
team site for colleagues, to an extranet site for partners, to an Internet site
for customers, people can share and publish information using one familiar
system.
The 2010 release does bring
a number of Web Content Management improvements:
- A more intuitive
content authoring/editing experience, with a similar look and feel to MS
Office
- Better support for
websites that need to be available in multiple languages
- Better organizing and
categorizing of content
- Improved search,
particularly via FAST Search, including more relevant results and more
ways to view the results
- Integration of Web
Analytics to see how your website is performing
- Personalization via
Audience targeting
- Cross browser Support —
view your site on most of the popular browsers today
2. Communities: Creating a Social
Collaboration Environment
Social capabilities like Facebook and Twitter are becoming normal for many
of us. Now all this social media stuff is moving into the workplace. It all
boils down to providing a modern approach to working together, collaborating
and sharing knowledge.
So these capabilities need
to be a component of every piece of software we use. SharePoint 2010 works
towards this goal by supporting:
- The
ability to create detailed user profiles (think employee Facebook pages)
- Use
of modern tools for sharing and collaboration including blogs and wikis.
- The
creation of special interest groups (Communities) to share knowledge or
work on projects
- Interactivity
via commenting and discussions around content items, and social
tagging/bookmarking of content
- The
creation of separate personal spaces or dashboards called MySites where
you can keep track of your own content, and the work you are doing in certain
communities, projects and more
3. Content:
Managing Your Documents, Information and Records
As part of Content
functionality in SharePoint, you have direct integration with your MS Office
environment, so you can work on your documents in a familiar environment.
SharePoint 2010 provides the
tools to help you work with both document and record management:
- Manage all of your
organization's documents and other information including controlling who
can read and update them.
- Categorize them for
easier search and retrieval.
- Mark them as official
records and lock them down from further changes.
4.
Search: The Google for Your Organization's Private Info
SharePoint 2010 has two
levels of search: the built in functionality which is greatly improved from
SharePoint 2007 and FAST Search, offering additional functionality. Out of the
box SharePoint search includes the ability to:
- Search for information
and people, including particular expertise
- Index content and data
stored outside of your SharePoint database
- Refine search results
based on taxonomy and metadata (how content is organized and
classified)
The addition of FAST Search
brings enhancements, including:
- View thumbnails and
previews of content within the result set
- Refine results based on
user profile or audience
- The ability to refine
search results with filters like Site, Author, Result Type and more
5.
Insights: Digging for Business Intelligence
A key goal in any business is staying ahead of the
competition. Increasingly, the class of software called Business Intelligence
plays an important role here. Business intelligence software is all about
helping you make decisions and find problems.
With this release you can:
- Use tools like Excel to gather and analyze data that
is stored in SharePoint
- Use SharePoint's native Excel Services engine to
crunch data and build web-based reports
- Pull together information from different systems and
present it in SharePoint
- Create dashboards, scorecards, and other views —
making key performance indicators widely accessible to information workers
and process managers
6.
Composites: Integrating Your Business Systems
Another big improvement for
SharePoint 2010 relates to its ability talk to — pushing and pulling data to/
from other business systems. Instead of having to work in multiple systems, you
can create composite applications in sharepoint.
Data integrations are key for management dashboards
and project management, but also for employees who may not need full access to
the business application. It's important to note that SharePoint 2010 can both
view and update external data via its Business Connectivity Services (BCS).
Version
History of SharePoint
|
Version
|
Year
|
Product
Names
|
|
|
1.0
|
2001
|
STS (SharePoint Team Services)
|
SPS 2001(SharePoint Product Services)
|
|
2.0
|
2003
|
WSS 2.0
|
SPS 2003
|
|
3.0
|
2006
|
WSS 3.0
|
MOSS 2007
|
|
2010
|
2010
|
SharePoint Foundation Server
|
SharePoint Server 2010
|
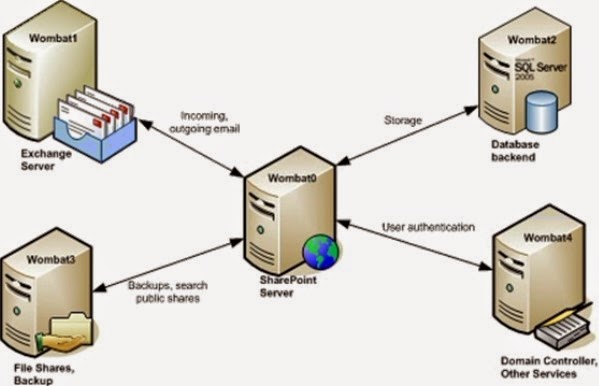
Role of SharePoint Server in a LAN Network.
Components of SharePoint
SharePoint
Foundation Server (Closest equivalent of WSS in 2007)
- Creating
team sites and collaborating on content within lists and libraries, or
features such as blogs, wikis, RSS feeds, alerts, and easy browser-based
customizations.
- It
provides developers with a great platform to build from. Out of the box,
it handles storage, web presentation, authorization, user management, and
has an interface into the Windows Workfow Foundation and because all of
this functionality is easily accessible through the object model, APIs,
and web services, it can greatly accelerate a developer’s job. Rather than
build all of those infrastructure pieces for every web-based product,
developers can leverage SharePoint Foundation and concentrate on just
building the solution.
Sharepoint
Server 2010
·
It extends Foundation server which is
automatically installed with SharePoint Server 2010
·
Its available in two editions: Standard Edition
& Enterprise Edition
o
Standard introduces core functionality like
social, search, and advanced web and enterprise content management.
o
Enterprise focuses primarily on adding
functionality through new service applications, introducing business
intelligence, line of business integration, reporting, and some Office client
services such as Visio.
Search
Server
- Foundation
server cannot pull search results from multiple site collection and cannot
add external content sources like file share or Exchange public folders
- Search Server 2010 Express (SSX) is a free
product from Microsoft that essentially takes SharePoint Foundation and
adds to it the intranet searching capabilities
- While
Search Server 2010 can be configured to avoid any single point of failure,
including the Search components
- It
can be deployed on only one server in the FARM and it’s not free
Fast
Search Sever:
- Visual
search and best bets
- Extreme
scale, with a billion documents possible
- Enhanced
multiple language capabilities
- Better
handling of unstructured data through metadata extraction
- Better
handling of structured data such as numbers, dates, etc.
SharePoint
Online (SharePoint Cloud)
- Another
push for SharePoint from Microsoft will be SharePoint in the cloud, hosted
by Microsoft. If you are looking to deploy SharePoint using this model,
the entire server infrastructure is hosted and maintained for you. This
model removes the administrative overhead of SharePoint and lets the
business focus just on using the power that is SharePoint.
Email
and Text Message (SMS) Service
- Can
be used for alerts
Application
Servers
- Query
Server: its responsible for responding to user search requests
- Index
Server: Also referred as Crawl Server.
- Excel
Service: It’s about supporting excel service in client browser.
- Usage
and Health Data Collection: It enables the collection of all the
diagnostic and usage data from your entire SharePoint farm in one
database.
Developers View of SharePoint
|


No comments:
Post a Comment